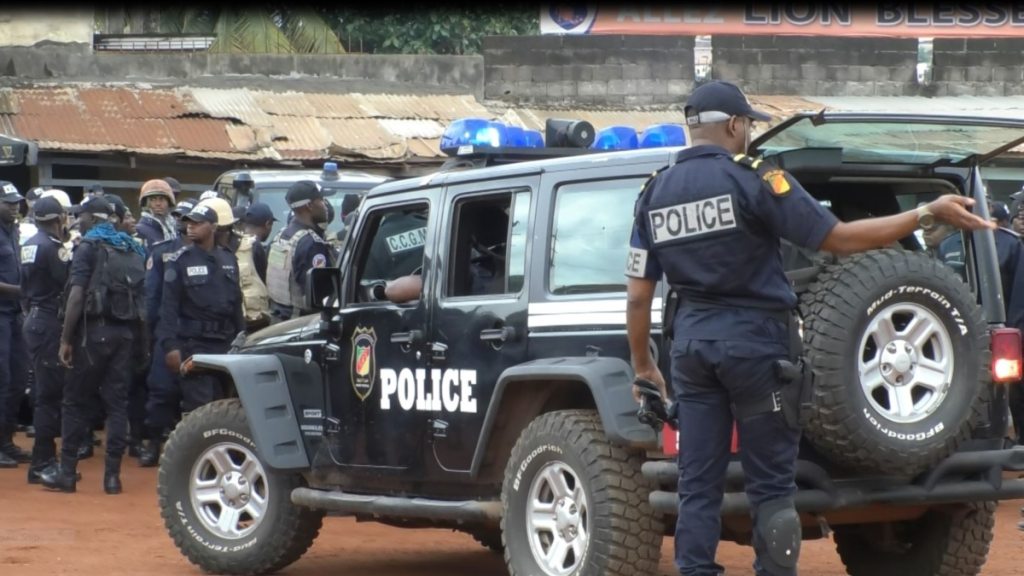
In recent events that garnered international attention, nearly 100 sexual and gender Minority Nigerians were arrested while attending a party. This unfortunate incident sheds light on the broader challenges faced by the LGBT community in Nigeria. Amidst high levels of poverty and socio-economic struggles, the Nigerian government’s strong anti-gay laws, compounded by the existence of Sharia laws in certain regions, exacerbate discrimination and inequality. This article delves deeper into the situation, highlighting the repercussions and missed opportunities for economic growth and development.

The Predicament of Poverty:
It is crucial to acknowledge that poverty is a pressing issue affecting the majority of Nigerians. With a large percentage of the population living in abject poverty, the focus of the government should ideally be on implementing policies and strategies that alleviate these conditions and foster sustainable economic growth. However, the plight of the LGBT community should not be neglected or exploited as a divisive tool; rather, it should be addressed within the broader context of social justice and human rights.
Anti-Gay Laws and Discrimination:
Nigeria maintains strong anti-gay laws that further marginalize the LGBT community. These laws not only violate basic human rights principles but also perpetuate stereotypes, prejudices, and discrimination. The criminalization of homosexuality undermines the fundamental pillars of equality, dignity, and individual freedoms. Particularly alarming are the sharia laws prevalent in certain regions, which further exacerbate the challenges faced by LGBT individuals. This discriminatory legal framework alienates and targets defenseless members of society instead of providing them the necessary protection and support they deserve.

Missed Opportunities and Diverted Focus:
While economic growth and development are vital for Nigeria’s progress, it is imperative for the government to prioritize the well-being and rights of all citizens, irrespective of their sexual orientation or gender identity. By targeting defenseless LGBT individuals, the Nigerian government not only perpetuates a hostile environment but also diverts attention and resources from more pressing issues that could positively impact the lives of all Nigerians. This misplaced focus harms the country’s social fabric and tarnishes its image internationally.
The Importance of Inclusivity:
Embracing inclusivity and protecting the rights of all citizens, regardless of their sexual orientation or gender identity, is not only a matter of morality and human rights but also a step towards creating a more harmonious and progressive society. Studies have demonstrated the positive correlation between LGBTQIA acceptance and economic growth, as societies that embrace diversity and inclusivity tend to attract individuals with diverse skills, talents, and perspectives, ultimately fostering innovation and economic development.
Promoting Dialogue and Change:
Advocacy, dialogue, and education play pivotal roles in challenging discriminatory laws and societal perceptions. By engaging in conversations and raising awareness about the challenges faced by the LGBT community, individuals and organizations can pave the way towards a more inclusive and accepting society. It is crucial to foster understanding, empathy, and respect, debunking myths and stereotypes associated with sexual orientation and gender identity.
The similarities of the situation of LGBT Nigerians and LGBT Cameroonians
While Nigeria and Cameroon are distinct countries with unique social and political landscapes, there are similarities in the challenges faced by LGBT individuals in both contexts. Here are some key similarities in the situation of LGBT Nigerians and LGBT Cameroonians:
* Discriminatory Legislation: Both Nigeria and Cameroon have laws in place that criminalize same-sex sexual activity. In Nigeria, Section 377 of the Nigerian Penal Code and the Same-Sex Marriage (Prohibition) Act serve as legal barriers to the rights and recognition of LGBT individuals. Similarly, Cameroon’s Penal Code includes provisions, such as Article 347 bis, that criminalize consensual same-sex conduct.
* Stigma and Social Exclusion: LGBT individuals in both Nigeria and Cameroon face widespread stigma and social exclusion due to deep-rooted cultural and religious beliefs regarding homosexuality. This stigma often leads to discrimination, harassment, and violence from individuals and communities, making it challenging for LGBT individuals to live openly and access basic services and opportunities.

How poverty and the low purchasing power of LGBT Nigerians play a disadvantage rile to their recognition in Nigeria by both the federal and state government.
Poverty and the low purchasing power of LGBT Nigerians significantly disadvantage their recognition in Nigeria by both the federal and state governments. Here’s how:
1. Limited Economic Influence: The low purchasing power of LGBT Nigerians limits their economic influence within society. Economic power often translates to political influence and the ability to advocate for rights and recognition. However, poverty disproportionately affects marginalized communities, hindering their ability to actively participate in the economic and political spheres. The lack of economic clout can make it more challenging for LGBT Nigerians to gain recognition and push for policy changes that protect their rights.
2. Barriers to Education and Employment: Poverty can create barriers to education and employment opportunities for LGBT individuals. Discrimination and stigmatization can result in reduced access to quality education and employment prospects, perpetuating a cycle of poverty. Without access to education or stable employment, LGBT Nigerians face challenges in increasing their economic well-being and social mobility. This further hampers their capacity to influence government policies and gain recognition.

3. Disproportionate Vulnerability: Poverty places LGBT Nigerians at a higher risk of facing various forms of discrimination, violence, and social exclusion. The lack of financial resources and social support networks can leave them more vulnerable to abuse and exploitation. This vulnerability can hinder the community’s ability to engage with government institutions, making it difficult for their voices to be heard and for their concerns to be addressed effectively.
4. Lack of Social Welfare Programs: In the face of poverty, social welfare programs become crucial for marginalized communities. However, the absence of specific programs targeted at supporting LGBT Nigerians further marginalizes them. A lack of supportive policies and resources within the government results in inadequate social protection measures, exacerbating the challenges faced by the community and deepening their invisibility.
5. Prevailing Social Attitudes: Poverty and low purchasing power intersect with prevailing social attitudes towards homosexuality to create a hostile environment for LGBT Nigerians in Nigeria. Negative societal attitudes fueled by cultural norms and religious beliefs contribute to their exclusion and marginalization. These attitudes influence government policies and pose barriers to recognizing and protecting the rights of the LGBT community.
Conclusion:
The recent arrest of close to 100 LGBT Nigerians attending a party brings to light the deep-rooted challenges faced by the LGBT community in Nigeria. The government’s strong anti-gay laws, coupled with socioeconomic struggles and misplaced priorities, perpetuate discrimination and hinder socio-economic development. It is imperative for the Nigerian government to focus on creating a more inclusive society that upholds human rights, fosters acceptance, and allocates resources to address poverty and inequality. By doing so, Nigeria can unlock its full potential, benefiting all its citizens and contributing to a more just and prosperous nation.